Yığın sıralaması
|
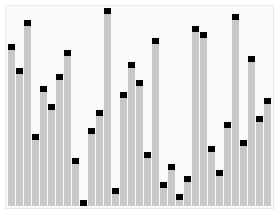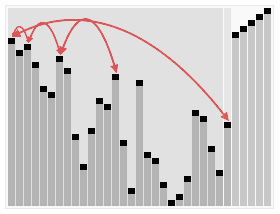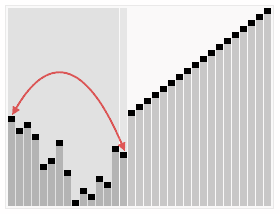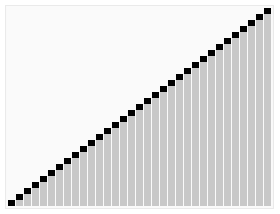
Yığın Sıralaması'nın rastgele üretilmiş sayıları nasıl sıraladığını gösteren örnek. Algoritmanın ilk aşamasında dizinin öğeleri yığın yapısını oluşturmak için yeniden sıralanır. | |
| Sınıf | Sıralama algoritması |
|---|---|
| Veri yapısı | Dizi |
| Zaman karmaşıklığı | O(n log n) |
| En iyi | Ara sıra |
| Alan karmaşıklığı | toplamda О(n), ek alan O(1) |
Yığın Sıralaması (İngilizcesi: Heapsort), bilgisayar bilimlerinde kullanılan karşılaştırmaya dayalı bir sıralama algoritmasıdır. Uygulamada pek çok bilgisayarda hızlı sıralama algoritmasından daha yavaş çalışsa da en kötü durumda O(n log n) çalışma süresi vardır. Yığın sıralaması diziyi yerinde sıralar ancak kararlı bir sıralama algoritması değildir.
Sözde Kodu
Aşağıda yığın sıralaması algoritmasının sözde kodu verilmiştir. swap dizideki iki öğenin yerlerini değiştirmek için kullanılmaktadır.
function heapSort(a, count) is
input: an unordered array a of length count
(first place a in max-heap order)
heapify(a, count)
end := count - 1
while end > 0 do
(swap the root(maximum value) of the heap with the last element of the heap)
swap(a[end], a[0])
(decrease the size of the heap by one so that the previous max value will
stay in its proper placement)
end := end - 1
(put the heap back in max-heap order)
siftDown(a, 0, end)
function heapify(a,count) is
(start is assigned the index in a of the last parent node)
start := (count - 1) / 2
while start ≥ 0 do
(sift down the node at index start to the proper place such that all nodes below
the start index are in heap order)
siftDown(a, start, count-1)
start := start - 1
(after sifting down the root all nodes/elements are in heap order)
function siftDown(a, start, end) is
input: end represents the limit of how far down the heap
to sift.
root := start
while root * 2 + 1 ≤ end do (While the root has at least one child)
child := root * 2 + 1 (root*2+1 points to the left child)
(If the child has a sibling and the child's value is less than its sibling's...)
if child < end and a[child] < a[child + 1] then
child := child + 1 (... then point to the right child instead)
if a[root] < a[child] then (out of max-heap order)
swap(a[root], a[child])
root := child (repeat to continue sifting down the child now)
else
return
heapify fonksiyonu alttan üste doğru bir yığın oluşturmak için kullanılırken yığın özelliği kazandırılmak için öğeler aşağıya doğru incelenir. Aşağıda gösterilmiş bir diğer yol kullanılarak yığın üstten alta oluşturulup öğeler yukarı doğru incelenebilir. Ancak aşağıdaki uygulama her ne kadar anlaşılması daha kolay olsa da daha yavaştır.
function heapify(a,count) is
(end is assigned the index of the first (left) child of the root)
end := 1
while end < count
(sift up the node at index end to the proper place such that all nodes above
the end index are in heap order)
siftUp(a, 0, end)
end := end + 1
(after sifting up the last node all nodes are in heap order)
function siftUp(a, start, end) is
input: start represents the limit of how far up the heap to sift.
end is the node to sift up.
child := end
while child > start
parent := ⌊(child - 1) ÷ 2⌋
if a[parent] < a[child] then (out of max-heap order)
swap(a[parent], a[child])
child := parent (repeat to continue sifting up the parent now)
else
return
Dış bağlantılar
- Bilgisayar Kavramları:Yığınlama Sıralaması (Hesap Sort)
- Analyze Heapsort in an online Javascript IDE
- Heapsort
- Heapsort animated
- NIST's Dictionary of Algorithms and Data Structures: Heapsort
- Sorting revisited
- Heapsort in C++ and explanation
- Java-based demonstration of Heapsort
- A graphical demonstration and discussion of heap sort